- Afhalen na 1 uur in een winkel met voorraad
- Gratis thuislevering in België vanaf € 30
- Ruim aanbod met 7 miljoen producten
- Afhalen na 1 uur in een winkel met voorraad
- Gratis thuislevering in België vanaf € 30
- Ruim aanbod met 7 miljoen producten
Zoeken
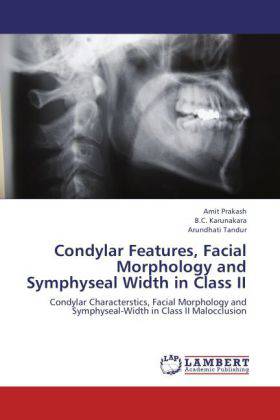
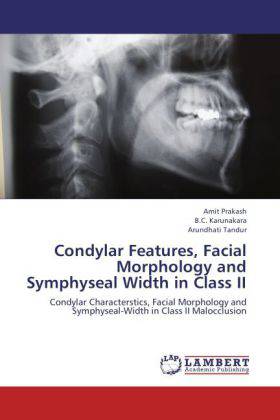
Condylar Features, Facial Morphology and Symphyseal Width in Class II
Condylar Characterstics, Facial Morphology and Symphyseal-Width in Class II Malocclusion
Amit Prakash, B. C. Karunakara, Arundhati Tandur
Paperback | Engels
€ 58,95
+ 117 punten
Omschrijving
Condylar head inclination proved to be the most significantly correlated condylar characteristics to facial morphology. Hypodivergent pattern is dominant in Class II malocclusion. Symphysis width dimension also vary in different Class II malocclusion.SBL-PNS, Y -axis, Facial -Axis, PFH/AFH X100, Bjork sum and Symphseal width are significant parameters which discriminate between groups. Horizontal facial morphology was seen in 45 % of cases, vertical 8.3% and normal was 46.7%. Facial types of the Class II patients vary and it depends on the position of the condyle in the fossa. It can be anteriorly or posteriorly placed, depending upon the type of jaw bases. Glenoid fossa position also changes; it can be cranially or caudally placed in class II patients depending upon skeletal facial types. Symphysis width was strongly related to the direction of mandibular growth. Symphysis width varies in different types of facial types. Generally it is wider in low angle subjects and narrow in high angle Class II preadolescent patients.
Specificaties
Betrokkenen
- Auteur(s):
- Uitgeverij:
Inhoud
- Aantal bladzijden:
- 100
- Taal:
- Engels
Eigenschappen
- Productcode (EAN):
- 9783659197024
- Verschijningsdatum:
- 26/07/2012
- Uitvoering:
- Paperback
- Afmetingen:
- 152 mm x 220 mm
- Gewicht:
- 159 g
Alleen bij Standaard Boekhandel
+ 117 punten op je klantenkaart van Standaard Boekhandel
Beoordelingen
We publiceren alleen reviews die voldoen aan de voorwaarden voor reviews. Bekijk onze voorwaarden voor reviews.