- Afhalen na 1 uur in een winkel met voorraad
- Gratis thuislevering in België vanaf € 30
- Ruim aanbod met 7 miljoen producten
- Afhalen na 1 uur in een winkel met voorraad
- Gratis thuislevering in België vanaf € 30
- Ruim aanbod met 7 miljoen producten
Zoeken
€ 108,45
+ 216 punten
Omschrijving
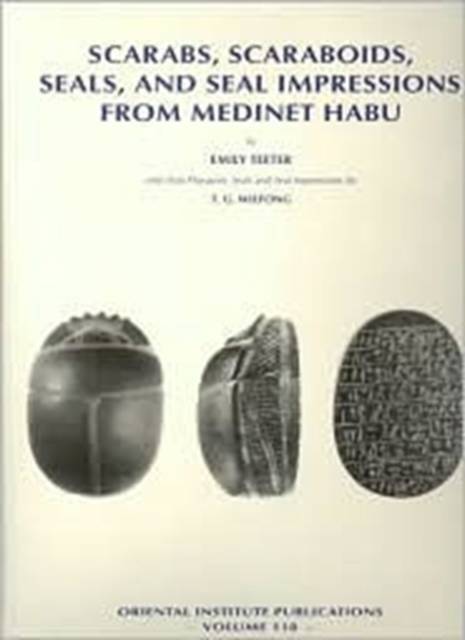
Medinet Habu in western Thebes (modern Luxor, Egypt) is dominated by the great mortuary temples of King Ramesses III (ca. 1182 BC), and Kings Aye and Horemheb (ca. 1324-1293 BC). It served as the seat of the regional government in the Late New Kingdom, and an important Coptic Christian community grew up within its great fortification walls. For nearly 1,500 years Medinet Habu played a central role in Egyptian religion, life, and politics. In 1924, the Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago began the documentation of Medinet Habu, but the last facet of the documentation - the publication of thousands of objects excavated at the site - was interrupted by World War II. This book, the first of a projected multiple volume series, marks the resurrection of the project to publish the small finds. It includes a catalogue of 349 scarabs, scaraboids (including lentoids, cowroids, and buttons), heart scarabs and their Sons of Horus amulets, heart amulets, seals, and seal impressions on bullae, vessel stoppers, amphora handles, mudbricks, and funerary cones that date from approximately 1470 BC to the eighth century AD. Each object is described and illustrated and, whenever possible, placed in its original archaeological context. These scarabs and scaraboids comprise one of the largest groups of such material excavated from any site in Egypt.
Specificaties
Betrokkenen
- Auteur(s):
- Uitgeverij:
Inhoud
- Aantal bladzijden:
- 272
- Taal:
- Engels
- Reeks:
- Reeksnummer:
- nr. 118
Eigenschappen
- Productcode (EAN):
- 9781885923226
- Verschijningsdatum:
- 15/08/2003
- Uitvoering:
- Hardcover
- Formaat:
- Genaaid
- Afmetingen:
- 234 mm x 308 mm
- Gewicht:
- 1859 g

Alleen bij Standaard Boekhandel
+ 216 punten op je klantenkaart van Standaard Boekhandel
Beoordelingen
We publiceren alleen reviews die voldoen aan de voorwaarden voor reviews. Bekijk onze voorwaarden voor reviews.